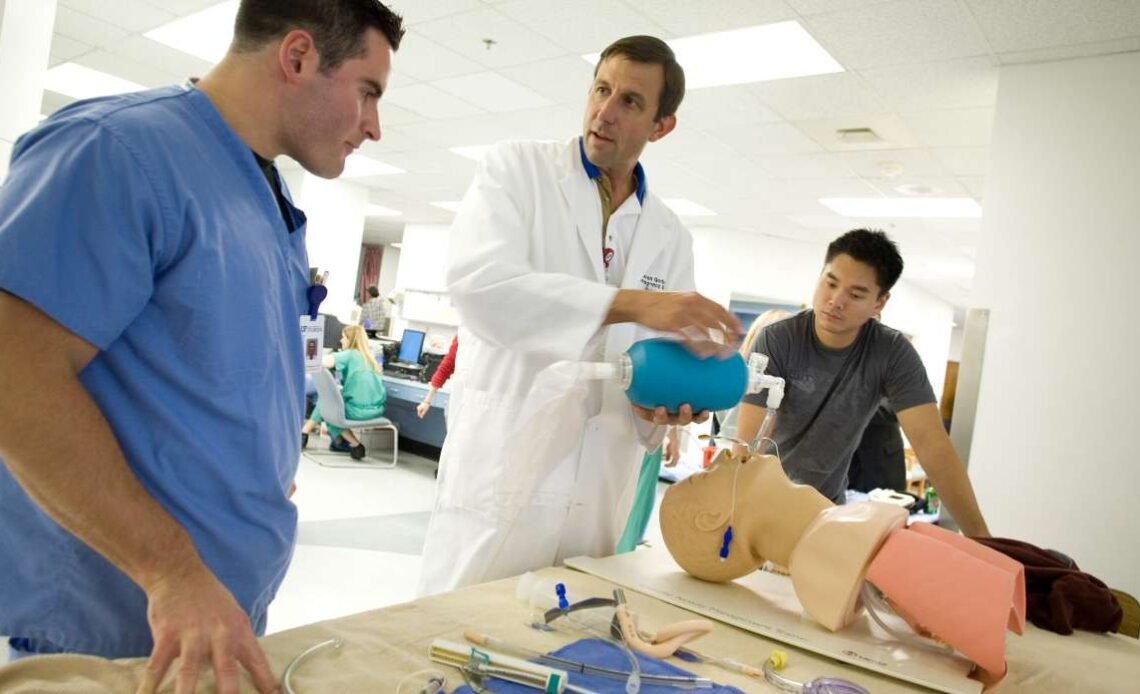
Medical training has traditionally relied on a combination of theoretical instruction, cadaver dissections, and clinical rotations to prepare students for the real-world challenges they will face as healthcare professionals. However, as medicine evolves and patient safety becomes increasingly prioritized, the use of realistic simulations in medical education has gained prominence. Among these, wound care simulations are particularly crucial. These simulations offer medical students and professionals a controlled yet lifelike environment to practice and hone their skills, bridging the gap between classroom learning and patient care. This blog post explores the importance of realistic wound care simulations in medical training, highlighting the benefits that are often overlooked in traditional medical education.
1. Enhancing practical skills and competency
Why practical skills matter:
Wound care is a fundamental aspect of medical practice, encompassing everything from minor cuts to complex surgical wounds and chronic ulcers. The ability to effectively assess, clean, dress, and manage wounds is critical for preventing infections, promoting healing, and ensuring patient well-being. Realistic wound care simulations provide a hands-on approach to mastering these essential skills.
Key benefits:
Hands-on experience: simulations allow students to practice wound care techniques on lifelike models, helping them develop the dexterity and precision required for real patient care. This includes tasks such as suturing, debridement, and applying various types of dressings.
Skill development: by repeatedly practicing on simulated wounds, students can refine their techniques, improving their ability to handle different types of wounds, from superficial abrasions to deep lacerations.
Competency assessment: instructors can use wound care simulations to assess students’ competency in a controlled environment. This enables targeted feedback and ensures that students are fully prepared before they encounter real patients.
Less discussed aspect: the role of simulations in developing fine motor skills is often overlooked. Wound care requires precision, particularly in tasks like suturing or applying delicate dressings. Realistic simulations provide the repetition needed to build these critical fine motor skills, which are difficult to develop through theoretical learning alone.
Stat to know: according to a study published in the journal of wound care, students who participated in realistic wound care simulations showed a 40% improvement in their practical skills compared to those who received traditional instruction alone.
2. Building confidence in wound management
Why confidence is critical:
Confidence plays a significant role in a healthcare professional’s ability to deliver effective care. In wound management, hesitation or uncertainty can lead to errors, patient discomfort, and delayed healing. Realistic wound care simulations help build the confidence needed to manage wounds efficiently and effectively.
Key benefits:
Safe learning environment: simulations provide a safe space for students to make mistakes and learn from them without the risk of harming a patient. This helps build confidence as students practice and refine their skills.
Exposure to a variety of scenarios: realistic simulations can replicate a wide range of wound types and complications, from acute trauma wounds to chronic diabetic ulcers. This exposure helps students develop the confidence to handle diverse and complex cases.
Repetition and mastery: the ability to repeat simulations multiple times allows students to master wound care techniques, reinforcing their confidence in their skills and decision-making abilities.
Less discussed aspect: the importance of building emotional resilience through simulations is often overlooked. Wound care, particularly in trauma or critical care settings, can be emotionally challenging. Simulations help students prepare for these emotional aspects by providing a realistic yet controlled environment in which to practice their responses.
Stat to know: a survey conducted by the american medical association (ama) found that 87% of medical students reported increased confidence in wound care management after participating in realistic simulations, underscoring the importance of these exercises in medical training.
3. Improving patient safety and outcomes
Why patient safety is paramount:
One of the primary goals of medical education is to prepare students to provide safe, effective care. Wound care simulations play a crucial role in achieving this goal by reducing the likelihood of errors in real clinical settings. By practicing on realistic models, students can perfect their techniques, leading to better patient outcomes.
Key benefits:
Error reduction: simulations allow students to practice and learn from their mistakes in a controlled environment, significantly reducing the risk of errors when treating actual patients. This is particularly important in wound care, where improper management can lead to infections or other complications.
Standardized training: realistic simulations ensure that all students receive consistent training in wound care, adhering to best practices and evidence-based protocols. This standardization helps maintain high levels of care across different healthcare settings.
Enhanced decision-making: simulations often include scenarios that require critical thinking and quick decision-making, such as managing a rapidly deteriorating wound. Practicing these scenarios helps students develop the ability to make informed decisions under pressure.
Less discussed aspect: the role of simulations in promoting interprofessional collaboration is often overlooked. Wound care often involves a multidisciplinary team, including doctors, nurses, and wound care specialists. Simulations that involve multiple healthcare roles can improve communication and collaboration, leading to better patient outcomes.
Stat to know: research published in the journal of patient safety found that students who engaged in wound care simulations were 50% less likely to make critical errors in real clinical settings compared to those who did not participate in simulations.
4. Bridging the gap between theory and practice
Why bridging the gap is important:
While theoretical knowledge is essential, the ability to apply that knowledge in real-world situations is what ultimately defines a competent healthcare professional. Realistic wound care simulations help bridge the gap between classroom learning and clinical practice, ensuring that students are well-prepared to deliver high-quality care.
Key benefits:
Application of theoretical knowledge: simulations provide an opportunity for students to apply what they’ve learned in lectures and textbooks to practical scenarios. This helps reinforce their understanding and improves knowledge retention.
Real-time feedback: during simulations, instructors can provide immediate feedback on students’ performance, helping them understand the practical implications of their theoretical knowledge and guiding them in areas that need improvement.
Increased engagement: hands-on simulations are more engaging than traditional lectures, helping to keep students motivated and invested in their learning. This increased engagement can lead to better learning outcomes.
Less discussed aspect: the use of simulations to teach students how to manage the psychological aspects of wound care is often overlooked. Patients with chronic wounds or traumatic injuries may experience significant emotional distress. Simulations can include these psychological elements, helping students learn how to provide holistic care that addresses both the physical and emotional needs of their patients.
Stat to know: a study in the british journal of surgery found that 93% of medical students believed that wound care simulations improved their ability to apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios, highlighting the effectiveness of this approach in medical training.
5. Adapting to emerging challenges in healthcare
Why adaptability is key:
Healthcare is constantly evolving, with new challenges and advancements emerging regularly. Realistic wound care simulations provide a flexible training platform that can be adapted to address current and future challenges in wound management.
Key benefits:
Incorporating new techniques: as new wound care techniques and technologies are developed, simulations can be updated to reflect these advancements, ensuring that students are trained in the latest best practices.
Preparing for future trends: simulations can be designed to address emerging trends in healthcare, such as the increasing prevalence of antibiotic-resistant infections or the rise of chronic conditions like diabetes that require specialized wound care.
Customized training: simulations can be tailored to meet the specific needs of different healthcare settings, from urban hospitals to rural clinics, ensuring that students are prepared to manage wounds in a variety of environments.
Less discussed aspect: the potential for simulations to incorporate virtual reality (vr) and augmented reality (ar) technologies is often overlooked. These technologies can enhance the realism of wound care simulations, providing students with an immersive learning experience that closely mimics real-world scenarios.
Stat to know: according to a report by deloitte, the use of vr and ar in medical training is expected to grow by 30% annually, with wound care simulations being a key area of application. This growth underscores the importance of adopting innovative technologies to enhance medical education.
Conclusion: the vital role of realistic wound care simulations in medical training
Realistic wound care simulations are an invaluable tool in medical training, offering students the opportunity to develop and refine their practical skills, build confidence, improve patient safety, and bridge the gap between theory and practice. As healthcare continues to evolve, these simulations will play an increasingly important role in preparing the next generation of healthcare professionals to meet the challenges of wound management.
By incorporating realistic wound care simulations into their curricula, medical schools and training programs can ensure that their students are not only knowledgeable but also proficient in the hands-on skills required to provide high-quality care. In doing so, they contribute to better patient outcomes, reduced healthcare costs, and a more resilient healthcare system.